Signal purity: Miniature antennas will help create underwater mobile communications
- Статьи
- Science and technology
- Signal purity: Miniature antennas will help create underwater mobile communications

Russian and Chinese experts have found a way to organize communication underwater using miniature devices. A prototype antenna with a length of about 15 cm has been created from a special composite material that propagates very low frequency waves over a distance of up to 100 m. The development opens the way to the creation of portable mobile communication systems for underwater vehicles, robots and scuba divers, experts believe.
How very low frequency waves break through the water column
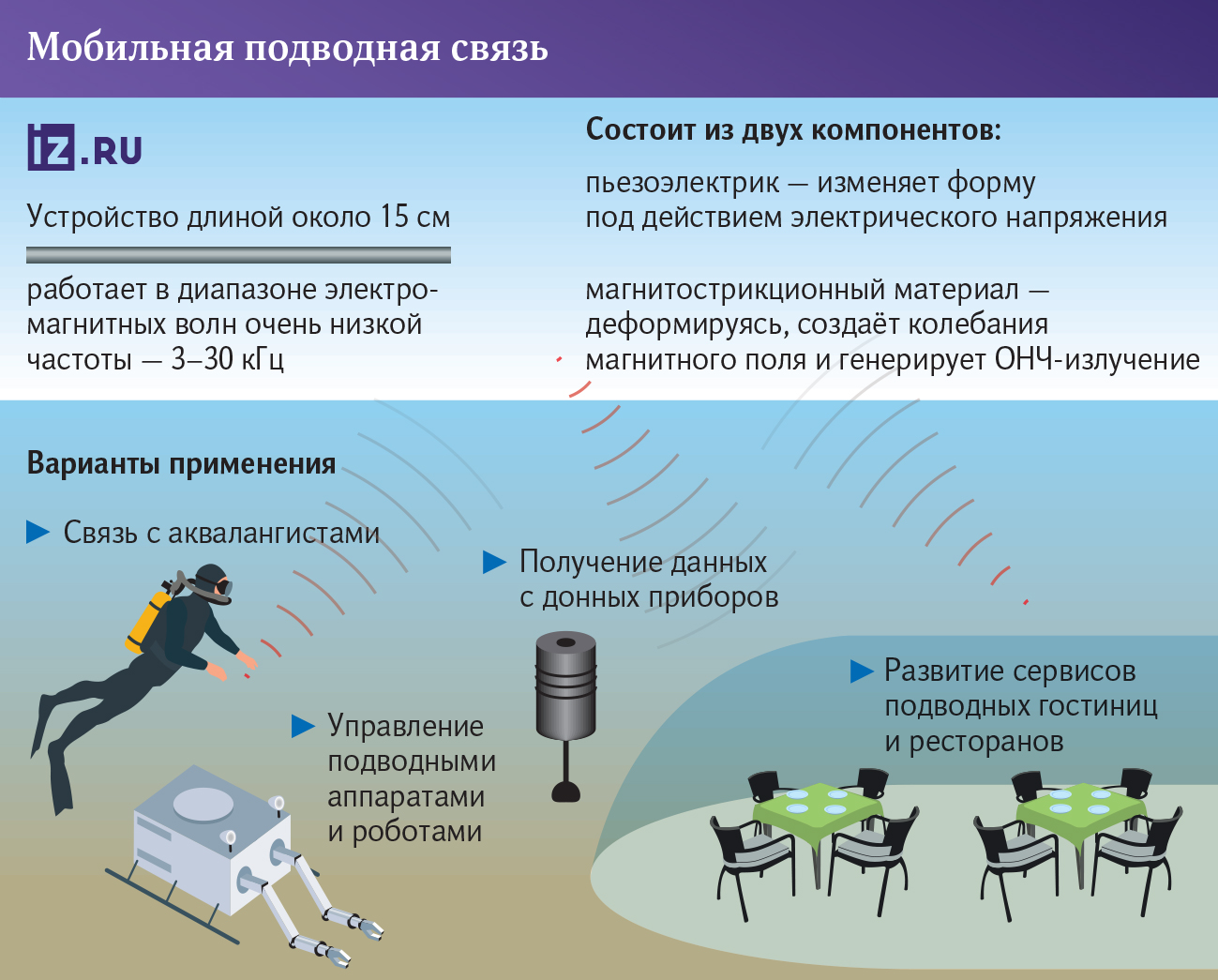
Scientists from the Polytechnic Institute of Novgorod State University, together with colleagues from a number of Chinese research organizations, have created a miniature antenna for underwater communications. With a length of about 15 cm, it is capable of transmitting a signal underwater at a distance of up to 100 m, which was previously impossible for such compact devices. The Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation told Izvestia about the invention.
As the researchers explained, the development promises a breakthrough in technologies for deep-sea applications. In particular, portable antennas of this type can be used for communication between scuba divers, control robots and autonomous devices.
— The innovation is based on a composite structure. It consists of a piezoelectric and a magnetostrictive material. The first of them, when an alternating electric voltage is applied to it, contracts and decompresses, creating vibrations. The second one, glued to the first one, is also deformed. As a result, its magnetic properties change. This creates an alternating magnetic field, which generates very low—frequency radiation in the surrounding space," Oleg Sokolov, a leading researcher at the Department of Radio Equipment Design and Technology at the Polytechnic Institute of NovSU, told Izvestia.
According to him, the usual underwater communication is practically inaccessible: radio waves in seawater fade quickly. Sound waves, which, for example, are used by dolphins and whales, solve this problem, but this method is sensitive to interference, prone to multipath propagation (echo) and characterized by a large signal delay. One of the solutions is very low frequency (VLF) radiation. Such electromagnetic waves are capable of penetrating water to a considerable depth. However, in this range, their length is tens of kilometers. This means that giant antennas are needed to generate radiation. A classic example is The VLF Transmitter Cutler in the USA. It provides communication with submarines anywhere in the world. At the same time, the complex covers an area of more than 8 square kilometers and consists of 12 masts, the main of which is higher than the Eiffel Tower. Such systems are not mobile and extremely expensive.
To circumvent the restriction, they are developing antennas where VLF radiation is created by rotating magnets, Oleg Sokolov added. But in such systems, it is difficult to control the rotation speed, and they also transmit data slowly.
How to create miniature underwater antennas
— Antennas that use the same principle as our development are more promising. In most composites, an improvement in the parameters of one component leads to a deterioration in the properties of the other. This contradiction was eliminated by adding modifying additives to the composition of classical piezoceramics. They include indium, niobium, manganese and antimony," Oleg Sokolov explained.
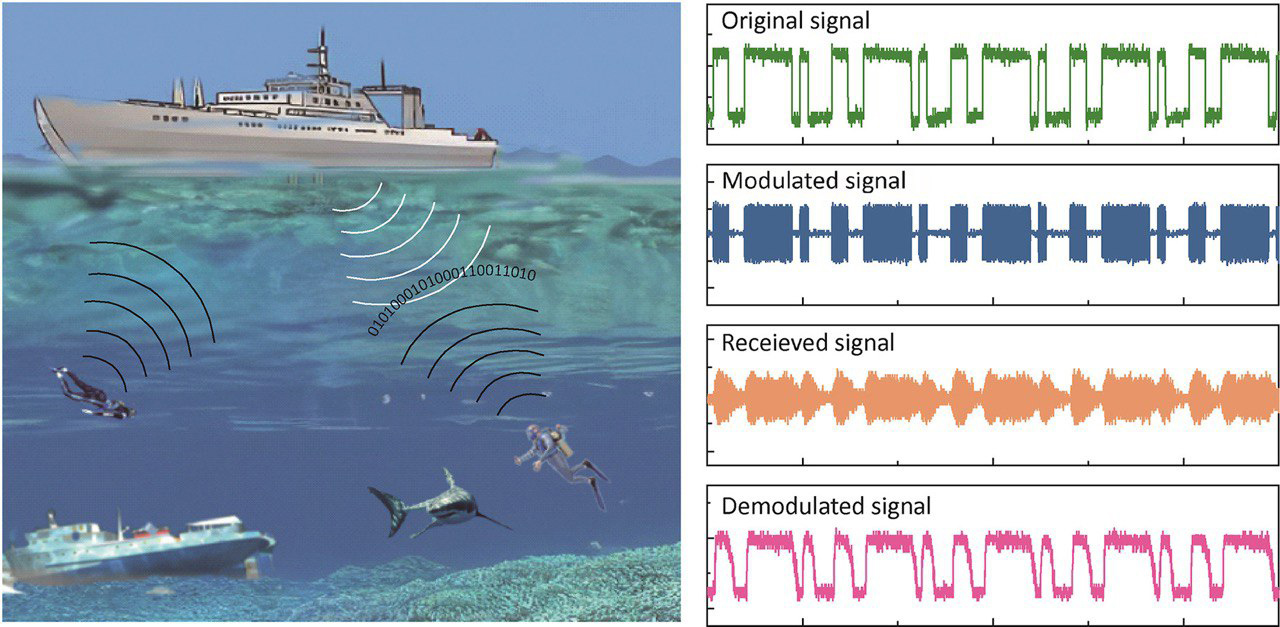
When testing a sample about 15 cm long, the experts recorded the magnetic field created by it at a distance of several meters. At the same time, the data transmission signal in the aquatic environment spread over 100 m, he said.
To show the system's performance, the scientists assembled an experimental mini-radio station and transmitted digital data and an analog signal (audio recording) over it. Both types of messages were successfully received and recognized.
According to Oleg Sokolov, in the future, the communication range under water can be increased due to new materials, as well as by increasing the antennas and combining them into arrays. Another way is to create a special geometry of transmitters.
— Underwater technology is intensively developing all over the world. But almost the only available method of communication between devices is sonar, the transmission of a signal by sound waves. However, this type of communication is energy—intensive and depends on many factors that are difficult to control," Oleg Kochetov, a researcher at the Laboratory of Ocean Acoustics at the P.P. Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, explained to Izvestia.
Compact magnetoelectric modems can open up new possibilities for underwater automata and robots, the expert noted.
— Thousands of scientists are working on reducing the size and increasing the power of underwater antennas in the world. But this task is limited by the rule that antenna efficiency is related to wavelength. Therefore, it has not yet been possible to make a small device for transmitting data over long distances," commented Ivan Malygin, professor at the Department of Radio Electronics and Communications at Ural Federal University.
According to him, if we assume the development of underwater tourism, hotels and restaurants, then the development makes sense and may be in demand.
— Similar developments are underway at the Krasnoyarsk Scientific Center for communication in mines. The presented work is a step forward in the development of compact underwater communications equipment, because the researchers managed to create a new material that made it possible to reduce the size of the radiator and increase the level of the radiated magnetic field," said Elena Strigova, senior lecturer at the Department of Radio Engineering at Siberian Federal University.
Nevertheless, the system operates in a narrow frequency band, which means it will not be able to transmit a large amount of data. According to her, such a solution can be used in the creation of compact systems for shallow depths. For example, for transmitting short messages and telemetry. In addition, the study lacks data on the operation of the system in real conditions. Therefore, it is difficult to talk about its effectiveness in various types of marine and freshwater reservoirs, especially at great depths. However, scientists are aware of these limitations and have outlined ways to improve the development.
— The proposed method is just one of the ways to generate a magnetic field underwater. The main problem is the high conductivity of salt water. If in a fresh environment it is about 0.01 Cm/m (Siemens per meter is a unit of measurement of electrical conductivity), then in a salty environment it can reach 4 Cm/m and higher. Because of this, the communication range drops. In our experiments, with a power consumption of 20-30 watts, it was possible to achieve a data transmission range of only about 7 m," explained the head of Laboratory No. 31 of Hydroacoustic Communication and Navigation Systems at the Institute of Problems of Marine Technologies. Academician M.D. Ageeva, Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Alexander Rodionov.
The expert stressed that the idea of combining piezoceramics and magnetostrictive material is interesting, but the developments need to be confirmed by real marine tests.
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»

